Update Sequence Value In Db2 Database Link
Much to the frustration of database administrators worldwide, prior to Oracle version 12c in mid-2014, Oracle simply had no inherent ability to inherently generate auto incrementing columns within a table schema. While the reasons for this design decision can only be guessed at, the good news is that even for users on older Oracle systems, there is a possible workaround to circumnavigate this pitfall and create your own auto incremented primary key column.
Creating a Sequence
The first step is to create a SEQUENCE in your database, which is a data object that multiple users can access to automatically generate incremented values. As discussed in the documentation, a sequence in Oracle prevents duplicate values from being created simultaneously because multiple users are effectively forced to “take turns” before each sequential item is generated.
For the purposes of creating a unique primary key for a new table, first we must CREATE the table we’ll be using:
Next we need to add a PRIMARY KEY constraint:
Finally, we’ll create our SEQUENCE that will be utilized later to actually generate the unique, auto incremented value.
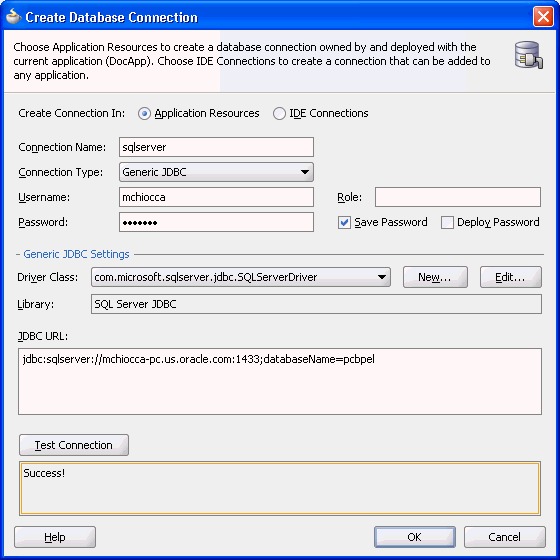
I can select a single NEXT VALUE from the sequence in an Input tool. A Post SQL statement that updates the -1s with the NEXT VALUE for.
Adding a Trigger
While we have our table created and ready to go, our sequence is thus far just sitting there but never being put to use. This is where TRIGGERS come in.
Similar to an event in modern programming languages, a TRIGGER in Oracle is a stored procedure that is executed when a particular event occurs.
Typically a TRIGGER will be configured to fire when a table is updated or a record is deleted, providing a bit of cleanup when necessary.
In our case, we want to execute our TRIGGER prior to INSERT into our books table, ensuring our SEQUENCE is incremented and that new value is passed onto our primary key column.
Here we are creating (or replacing if it exists) the TRIGGER named books_on_insert and specifying that we want the trigger to fire BEFORE INSERT occurs for the books table, and to be applicable to any and all rows therein.
The ‘code’ of the trigger itself is fairly simple: We SELECT the next incremental value from our previously created books_sequenceSEQUENCE, and inserting that into the :new record of the books table in the specified .id field.
Note: The FROM dual part is necessary to complete a proper query but is effectively irrelevant. The dual table is just a single dummy row of data and is added, in this case, just so it can be ignored and we can instead execute the system function of our trigger rather than returning data of some kind.
IDENTITY Columns
IDENTITY columns were introduced in Oracle 12c, allowing for simple auto increment functionality in modern versions of Oracle.
Using the IDENTITY column is functionally similar to that of other database systems. Recreating our above books table schema in modern Oracle 12c or higher, we’d simply use the following column definition.
- DB2 Tutorial
- DB2 Useful Resources
- Selected Reading
This chapter introduces you to the concept of sequence, creation of sequence, viewing the sequence, and dropping them.
Introduction
A sequence is a software function that generates integer numbers in either ascending or descending order, within a definite range, to generate primary key and coordinate other keys among the table. You use sequence for availing integer numbers say, for employee_id or transaction_id. A sequence can support SMALLINT, BIGINT, INTEGER, and DECIMAL data types. A sequence can be shared among multiple applications. A sequence is incremented or decremented irrespective of transactions.
A sequence is created by CREATE SEQUENCE statement.
Types of Sequences
There are two type of sequences available:
NEXTVAL: It returns an incremented value for a sequence number.
PREVIOUS VALUE: It returns recently generated value.
Parameters of sequences
The following parameters are used for sequences:
Data typePokemon gba. : This is the data type of the returned incremented value. (SMALLINT, BIGINT, INTEGER, NUMBER, DOUBLE)
START WITH: The reference value, with which the sequence starts.
MINVALUE: A minimum value for a sequence to start with.
MAXVALUE: A maximum value for a sequence.
INCREMENT BY: step value by which a sequence is incremented.
Sequence cycling: the CYCLE clause causes generation of the sequence repeatedly. The sequence generation is conducted by referring the returned value, which is stored into the database by previous sequence generation.
Creating a sequence
You can create sequence using the following syntax:
Syntax:
Example: [To create a new sequence with the name ‘sales1_seq’ and increasing values from 1]
Viewing the sequences
You can view a sequence using the syntax given below:
Syntax:
Example: [To see list of previous updated value in sequence ‘sales1_seq’]
Output:
Dropping the sequence
To remove the sequence, you need to use the “DROP SEQUENCE
Syntax:
Example: [To drop sequence ‘sales1_seq’ from database]
Output: